Technological development is the critical factor in the radical restructuring of the last-mile delivery segment, as deliveries are now completed in an increasingly new mode. According to the latest statistics, the need for an effective last-mile delivery service is exceptionally high, and consumers now prefer fast and accurate deliveries more than they ever do.
As online ordering and eCommerce are growing fast, courier delivery companies are now obligated to deliver parcels smoothly and within a short time. Technology has been a driving force in the shipping business evolution owing to disruptive innovations involving route optimization algorithms, GPS tracking systems, and real-time delivery updates becoming essential instruments for modern delivery operations.
These breakthroughs improve efficiency, decrease shipping industry costs, and provide consumers with a better shopping experience. Today’s Customers have already gotten used to getting their goods with a decent level of transparency, convenience, and speed, which has consequently created a demand for breakthrough solutions, especially last-mile deliveries.
This blog explores how last-mile delivery apps are reinventing the shipping sector, enabling businesses to meet the escalating consumer expectations while at the same time ushering in a new era of courier delivery where the order is sent straight to the customer’s doorstep.
What is Last-mile Delivery?

Last-mile delivery apps are digital platforms or software devices that are created to maximize the final stage of the delivery process to obtain delivery of goods from distribution centres to the doorsteps of end customers promptly and on time.
The apps utilize emerging features such as GPS tracking, route calculation algorithms, and real-time tracking to improve operations and boost customer satisfaction.
Key Points about Last Mile Delivery Apps:
- It is an application committed to last-mile deliveries that offer customers an excellent opportunity to monitor the progress of their deliveries in real time.
- Sophisticated algorithms within such apps are developed to strategize delivery routes using the data regarding traffic situations, delivery priorities, and distances, reducing delivery vehicles’ time and fuel consumption.
- Customers get an instant notification about their delivery status by using the app, where they get information like the delivery time, expected arrival time, and any possible delays if they occur.
- Most last-mile delivery apps provide a function called proof of delivery; this includes either electronic signatures or photo evidence to verify the last leg of delivery has been completed, and a delivery record is created.
For instance, UberEats, one of the most recognized last-mile delivery apps, connects customers with restaurants and delivers orders directly to their doorsteps. The platform has features that make up a smooth and easy food delivery service: live tracking and delivery notifications.
Last-mile delivery applications are now the pivots of shipping companies, serving as the brains of the operation, cost reduction and logistics systems that help businesses cater to the demand for fast and reliable deliveries in the digital age.
Searching for a perfect solution to launch your last-mile delivery application?
How Does the Last Mile Delivery Work?

Both businesses and consumers must understand the workings of last-mile delivery to make sense of it. In this final stage of the delivery journey, the operations become complex and coordinated to ensure that packages reach the desired destinations on time and effectively.
Order Processing
- The movement starts with a customer ordering via an online website or application.
- The team features a logistics department responsible for processing shipment details such as the delivery address and package specifications.
Warehouse Fulfillment
- When the order is done with the processes, it is arranged and delivered to the nearest depot.
- Inventory management systems are responsible for selecting the right products and ensuring their timely delivery.
Dispatching Delivery Vehicles
- After the order is ready, the delivery car, usually a van or a bike, is shipped to pick up the package.
- Routes for delivery are optimized in a way that decreases the time of travel and guarantees that all goods will be delivered on time.
Driver Pick-up and Route Navigation
- The delivery driver starts at the distribution centre to have the package and then uses the navigation or an app to find the most optimal route for last-mile delivery.
- Tracking in real-time allows customers and the shipping department to keep up with the shipment’s progress.
Customer Delivery
- The final step in the delivery journey is taken by the delivery driver crossing the final leg and delivering the package to the customer herself.
- Consequently, the delivery companies could ask for a signature or photo confirmation from the recipient as proof of delivery.
To be more specific, the last leg of the shipment is the last but not the most miniature stage that guarantees the timely delivery of packages. Through technology integration, intelligent logistics management, and carefully crafted routes, businesses can fasten up their last-mile delivery because of the growing demand for fast, reliable deliveries in a cut-throat market.
Interesting Ways Technology Can Foster Last-mile Delivery Operations
However, last-mile delivery operations face numerous hurdles, and technology provides intriguing alternative options that can significantly improve performance and productivity. Through thoughtful route planning to the application of drones, automatic cars, and other upcoming technologies, the future delivery process is likely to be reshaped, offering businesses the opportunity to simplify operations and better meet customer demands.
Smart Route Planning
Smart route planning uses data analytics, practical information, and real-time data to develop the most optimum delivery routes. Through the process that evaluates travel time, traffic condition, delivery schedule, and package importance, such technology reduces travel time, fuel consumption, and delivery costs and simultaneously increases on-time deliveries.
Route Optimization
These optimization algorithms for routes do not just go a step far as they dynamically change routes based on the occurring variations. The algorithms run these algorithms to analyze the traffic, the weather conditions, and the delivery volumes, which assists in selecting the most efficient and timely routes and improves overall delivery performance.
Drone Delivery
Drone delivery is an innovative game-changer for the topmost segment of the logistics process. Drones with precise navigational systems will enter with the package capacity and lead the way in swift food delivery of small packages directly to customers’ doors.
Companies such as Wing and Amazon Prime Air have transported goods such as drugs, food, household items, laundry, and finished goods quickly and contactless through deliveries in cities or other remote locations.
Tow Wing, a start-up of Alphabet Inc., has sparked a last-mile delivery innovation with its drone technology. Wing’s drones can carry small packages that do not exceed a few pounds and cover the distance quickly; hence, they are a perfect fit for urgent deliveries.
The significant advantage of drones lies in fast delivery times and less environmental impact caused by fewer emissions than those of conventional vehicles.
Automatic Vehicles
The application of autonomous vehicles, including self-driving cars/trucks, offers last-mile delivery operations a great chance to be improved. Such machines can drive urban surroundings without [any] violations of traffic regulations while providing different routes for convenient deliveries.
By reducing human error and labour costs, autonomous vehicles are a solution to the logistics sector so that the future is fully automated last-mile delivery.
Micro Fulfilment Centres
Fulfilment centres near urban or high-demand areas are strategically used to reduce the time required for order processing and delivery. With these small warehouses, automation is employed to increase the speed of picking, packing, and shipping.
Through it, businesses can stay on track with the ever-growing market of same-day and next-day deliveries at no additional cost.
Using these cutting-edge technologies in the last-mile delivery of products also resolves existing challenges and, at the same time, helps to set up sustainability, efficiency, and customer-centricity in future delivery systems.
Role of Last Mile Deliveries in Fostering Customer Experiences
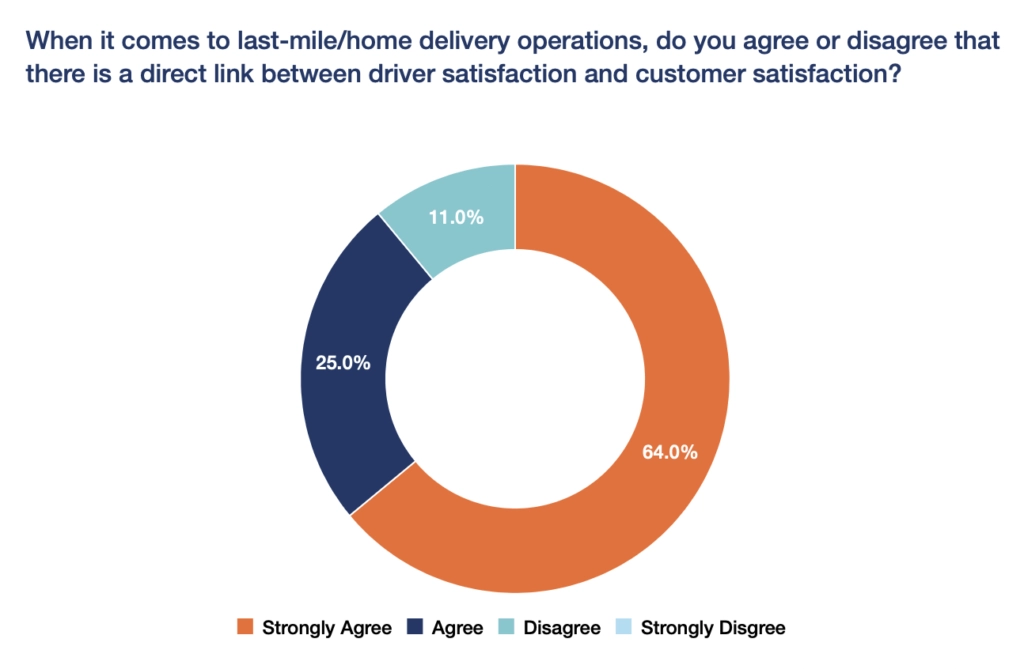
Source: Talking Logistics
Today, in a world where eCommerce prevails, businesses emphasise the consumer experience. It is the experience of a customer that creates brand loyalists and eventually paves the path for business success.
Given the growing trend towards online shopping, which highlights the convenience of delivery and accessibility to consumers, we cannot but absolve the importance of last-mile delivery in providing excellent customer experiences.
- On-time delivery has become sort of a trump card in today’s standards of the customer experience.
- After analyzing the latest data, it can be concluded that more than 80 per cent of online customers have a positive attitude toward fast delivery, which is one of the main reasons for their buying preferences.
- Delivering goods quickly helps businesses meet deadlines and boosts customer satisfaction, encouraging repeat business.
Swift deliveries are not thought of as just meeting delivery deadlines. They give the customers the thrill they are looking for. When orders are processed fast and effortlessly, your customers automatically consider themselves essential and notice an improved overall shopping experience. This positive engagement is one of the keys to fostering trust and loyalty, which will result in customers being retained and of goodwill.
Imagine that a customer wants to send a gift to someone at a special event. Instead of a made-to-wait last-mile delivery, the gift will arrive on time and pleasantly surprise the recipient at the last moment, reinforcing the commonly known impressions. These situations, in particular, play a crucial role in raising the bar for overall client satisfaction and contribute significantly to the prestige of the brand and the customer’s loyalty to it.
The role of last-mile deliveries in creating customer interactions cannot be stressed enough. Through fast and efficient deliveries, enterprises can establish memorable interactions, robust customer relationships, and differentiation that attracts more people to the business.
Final Thoughts
Last-mile delivery operations have already learned how to play a role in the current shipping environment, and they promise even more significant influence as they continue shaping the industry. With continuous preference for quick and dependable services of final-mile deliveries by customers, the last mile shipping is still under the spotlight, fostering innovation and transformation in the logistics industry.
One way of effective demand fulfilment with time is advanced delivery services, which utilize robust delivery platforms and technologies. These platforms streamline routes and advance the industry’s operational effectiveness; ultimately, they put customers’ interests first to bring improved business results.
If your business is getting ready for delivery platform development or you are looking for opportunities to improve the last-mile delivery system, our product is what you need. Being an organization with proven capabilities in providing unique and customized solutions can enhance your ability to satisfy customers with top shipping services while outdoing your competition.
Contact us and infuse the horizon of last-mile deliveries; together, we will find new splendour in shipping and customer experience.
Frequently Ask Questions
Last mile delivery refers to the final step in the delivery process,
where goods are transported from a distribution center or transportation
hub to the final customer. It’s often the most complex and costly part
of the shipping process, and it plays a critical role in ensuring fast
and efficient delivery.
The main features of last mile delivery apps include:
- Real-Time Tracking: Enables customers to track their
deliveries in real-time.
- Route Optimization: Algorithms that determine the fastest
and most efficient routes.
- Delivery Scheduling: Allows customers to select delivery
time slots or reschedule.
- Payment Integration: Easy payment gateways for smooth
transactions.
- Push Notifications: Alerts for delivery status updates,
delays, or package arrivals.
- Driver Communication: In-app messaging or calling
features between drivers and customers.
- Customer Feedback: Allowing customers to rate and review
delivery experiences.
- Real-Time Tracking: Enables customers to track their deliveries in real-time.
- Route Optimization: Algorithms that determine the fastest and most efficient routes.
- Delivery Scheduling: Allows customers to select delivery time slots or reschedule.
- Payment Integration: Easy payment gateways for smooth transactions.
- Push Notifications: Alerts for delivery status updates, delays, or package arrivals.
- Driver Communication: In-app messaging or calling features between drivers and customers.
- Customer Feedback: Allowing customers to rate and review delivery experiences.
Businesses benefit from last mile delivery apps by:
- Faster Deliveries: Reducing delivery times and improving
on-time delivery rates.
- Cost Savings: Optimizing delivery routes and reducing
fuel and operational costs.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Offering real-time
tracking, notifications, and more flexible delivery options.
- Better Data Analytics: Gathering insights about delivery
performance, customer preferences, and operational
inefficiencies.
- Faster Deliveries: Reducing delivery times and improving on-time delivery rates.
- Cost Savings: Optimizing delivery routes and reducing fuel and operational costs.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Offering real-time tracking, notifications, and more flexible delivery options.
- Better Data Analytics: Gathering insights about delivery performance, customer preferences, and operational inefficiencies.
Some common challenges in last mile delivery include:
- Traffic Congestion: Urban traffic can delay deliveries
and increase costs.
- Delivery Failures: Issues with incorrect addresses,
missed deliveries, or inaccessible locations.
- Costly Operations: Managing fuel, vehicle maintenance,
and driver salaries can be expensive.
- Scalability: As businesses expand, scaling last mile
delivery operations can be a challenge.
- Traffic Congestion: Urban traffic can delay deliveries and increase costs.
- Delivery Failures: Issues with incorrect addresses, missed deliveries, or inaccessible locations.
- Costly Operations: Managing fuel, vehicle maintenance, and driver salaries can be expensive.
- Scalability: As businesses expand, scaling last mile delivery operations can be a challenge.
Last mile delivery apps address delivery failures by:
- Improved Address Verification: Ensuring that customers
provide accurate addresses through automated checks.
- Customer Communication: Real-time alerts to customers
about delays or when the delivery is on the way, minimizing
missed deliveries.
- Alternative Delivery Options: Offering lockers, drop-off
points, or alternate delivery times to ensure a successful
delivery.
- Improved Address Verification: Ensuring that customers provide accurate addresses through automated checks.
- Customer Communication: Real-time alerts to customers about delays or when the delivery is on the way, minimizing missed deliveries.
- Alternative Delivery Options: Offering lockers, drop-off points, or alternate delivery times to ensure a successful delivery.
There are several last mile delivery models that businesses use:
- Crowdsourced Delivery: Using freelance drivers or
independent contractors to handle deliveries.
- Dedicated Delivery Fleet: A company-owned fleet of
drivers and vehicles managing deliveries.
- Local Delivery Networks: Smaller, more localized delivery
networks that can provide faster service to specific regions.
- Automated Delivery: The use of robots, drones, or
autonomous vehicles to make deliveries, reducing human labor
costs.
- Crowdsourced Delivery: Using freelance drivers or independent contractors to handle deliveries.
- Dedicated Delivery Fleet: A company-owned fleet of drivers and vehicles managing deliveries.
- Local Delivery Networks: Smaller, more localized delivery networks that can provide faster service to specific regions.
- Automated Delivery: The use of robots, drones, or autonomous vehicles to make deliveries, reducing human labor costs.
Last mile delivery apps improve customer experience by:
- Providing Real-Time Tracking: Customers can track their
packages from dispatch to delivery.
- Offering Flexible Delivery Options: Customers can choose
their preferred time slot or delivery location.
- Personalized Communication: Sending customized
notifications and alerts for estimated delivery times and status
updates.
- Easy Returns: Allowing customers to schedule pick-ups for
returns directly through the app.
- Providing Real-Time Tracking: Customers can track their packages from dispatch to delivery.
- Offering Flexible Delivery Options: Customers can choose their preferred time slot or delivery location.
- Personalized Communication: Sending customized notifications and alerts for estimated delivery times and status updates.
- Easy Returns: Allowing customers to schedule pick-ups for returns directly through the app.
Several technologies enable last mile delivery apps to function
efficiently:
- GPS and Geolocation: To track and optimize delivery
routes in real-time.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): For predicting delivery
times, optimizing routes, and enhancing customer experience.
- Machine Learning: To improve delivery predictions and
optimize fleet management.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Enabling real-time tracking of
packages, vehicles, and drivers.
- Cloud Computing: For data storage and seamless
integration across multiple devices and platforms.
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency and security in the
delivery process, especially for high-value goods.
- GPS and Geolocation: To track and optimize delivery routes in real-time.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): For predicting delivery times, optimizing routes, and enhancing customer experience.
- Machine Learning: To improve delivery predictions and optimize fleet management.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Enabling real-time tracking of packages, vehicles, and drivers.
- Cloud Computing: For data storage and seamless integration across multiple devices and platforms.
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency and security in the delivery process, especially for high-value goods.
The future of last mile delivery apps is driven by:
- Autonomous Vehicles and Drones: The use of self-driving
cars and delivery drones to further reduce costs and delivery
times.
- Sustainability: The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs)
and green delivery solutions to reduce the carbon footprint.
- Hyperlocal Delivery Models: Localized delivery hubs that
reduce distances and speed up deliveries.
- Enhanced AI Capabilities: Advanced AI for better route
optimization, real-time data analytics, and predictive delivery
times.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Drones: The use of self-driving cars and delivery drones to further reduce costs and delivery times.
- Sustainability: The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and green delivery solutions to reduce the carbon footprint.
- Hyperlocal Delivery Models: Localized delivery hubs that reduce distances and speed up deliveries.
- Enhanced AI Capabilities: Advanced AI for better route optimization, real-time data analytics, and predictive delivery times.